Potential Savings Upon Conversion
As the datacenter industry receives increased attention regarding their resource consumption, it has become advantageous to seek out components which minimize consumption, while maintaining expected performance and maximize existing resources.
The graphs below display a comparison between Sepolina, Octofreeze's cooling system, and other common commercially available cooling systems.
The information used for competing cooling systems was taken directly from their manufacturer and is available by request. The ambient conditions used for this estimate are: ambient temperature 40 C and 21% RH. The electricity cost was estimated to be $0.08 / kWH. The assumed annual operating hours as 8,760 (24 hrs. x 365 days).
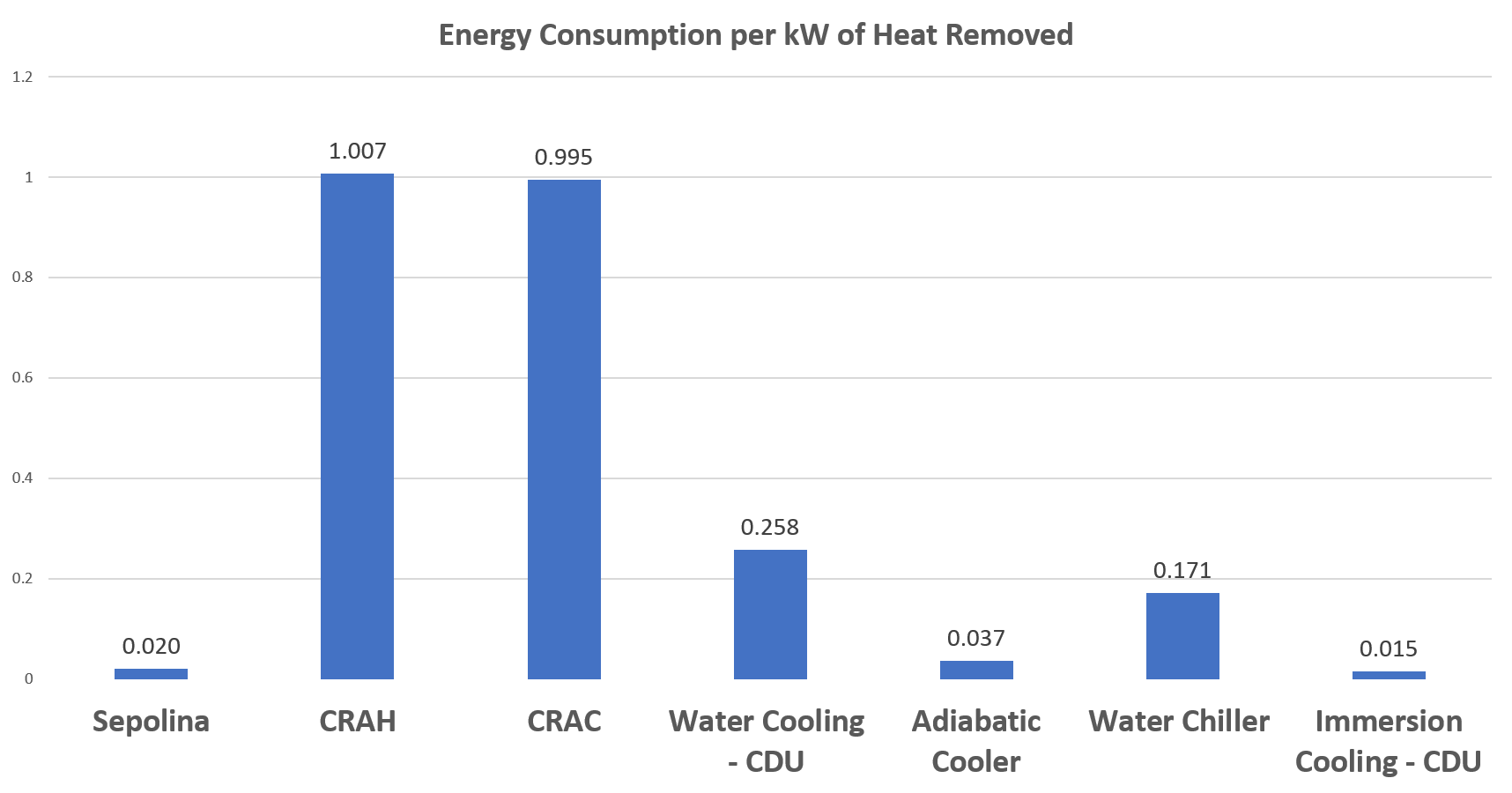
The graph above shows a comparison of energy consumed to remove one kilowatt of heat. Our solution Sepolina placed first and other commercially available cooling systems following.
As you can see, Sepolina operates as the lowest energy consuming complete cooling system package. The closest commercially available systems require coupling to an additional method to complete the cooling process.
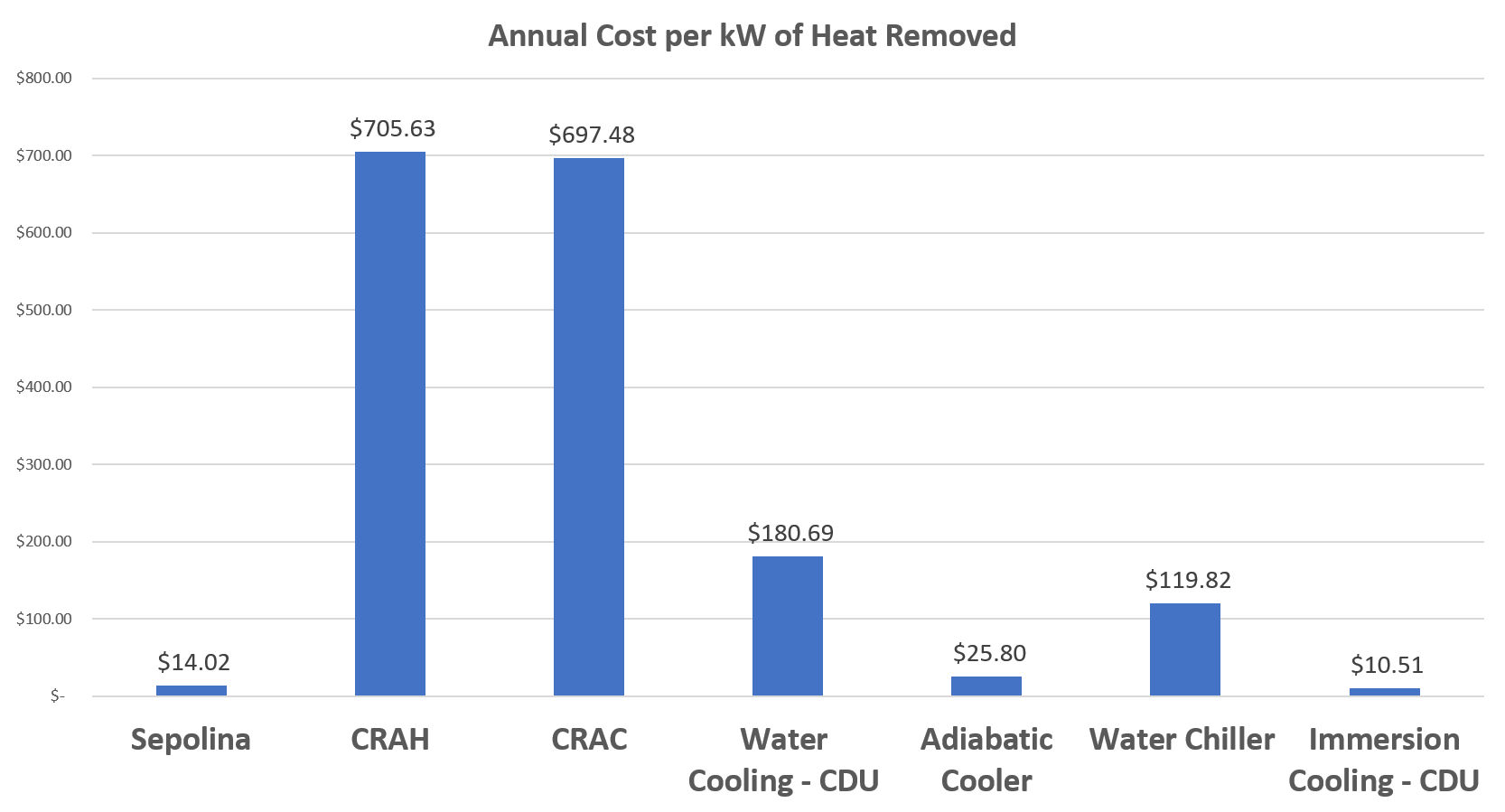
In this graph, a calculated annual cost to remove one kilowatt of heat was performed based on estimated electricity price per hour, cooling system consumption results from the previous graph and the assumed annual operating hours.
As you can see, Sepolina operates with the lowest annual cost for a complete cooling system package. The closest commercially available systems require coupling to an additional method to complete the cooling process.
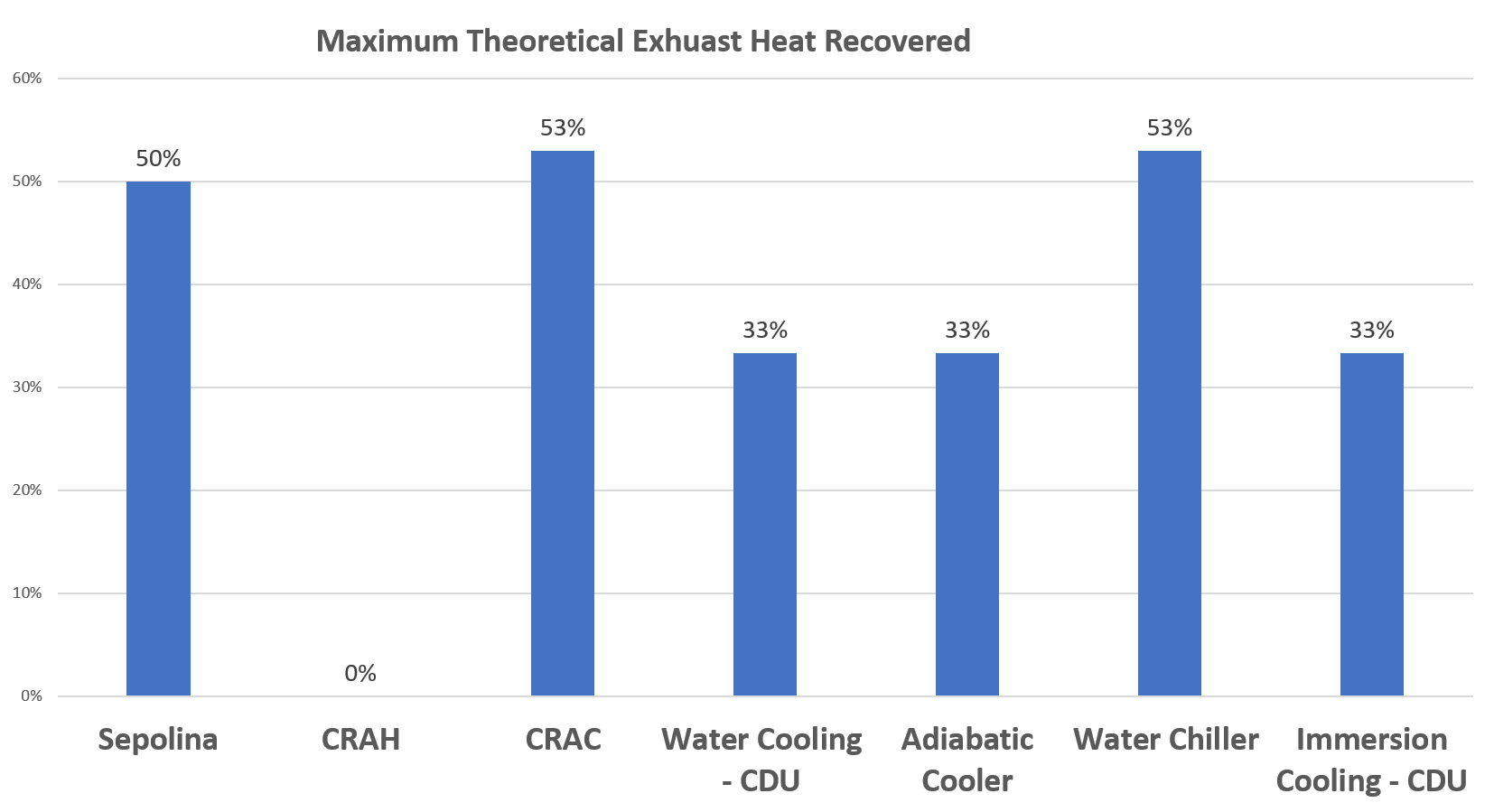
This graph shows a maximum theoretical percentage of exhaust heat that could be recovered by each cooling system. This calculation was performed using Carnot efficiency, where the ambient temperature is the cold value and the highest temperature each cooling system experiences as the cold value.
This graph, while idealistic displays the trend of which cooling systems would provide the most benefit when aided by an exhaust heat recovery system. Also, this value is used within the next two calculations to further prove the overall point of maximizing existing resources.
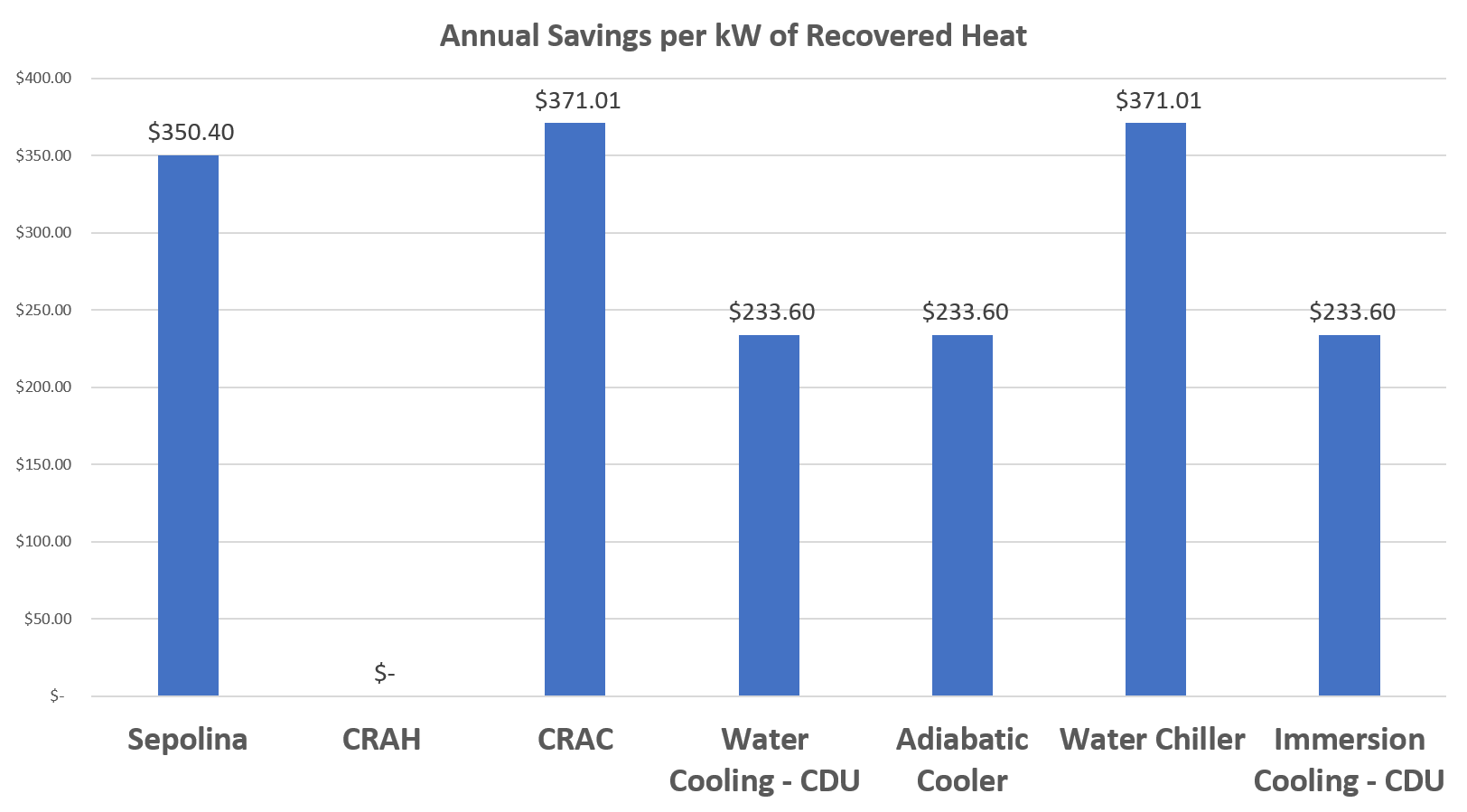
This graph shows the potential annual savings, per kilowatt of recovered exhaust heat based on the theoretical maximum recovery rate and the estimated price of electricity, for each cooling system.
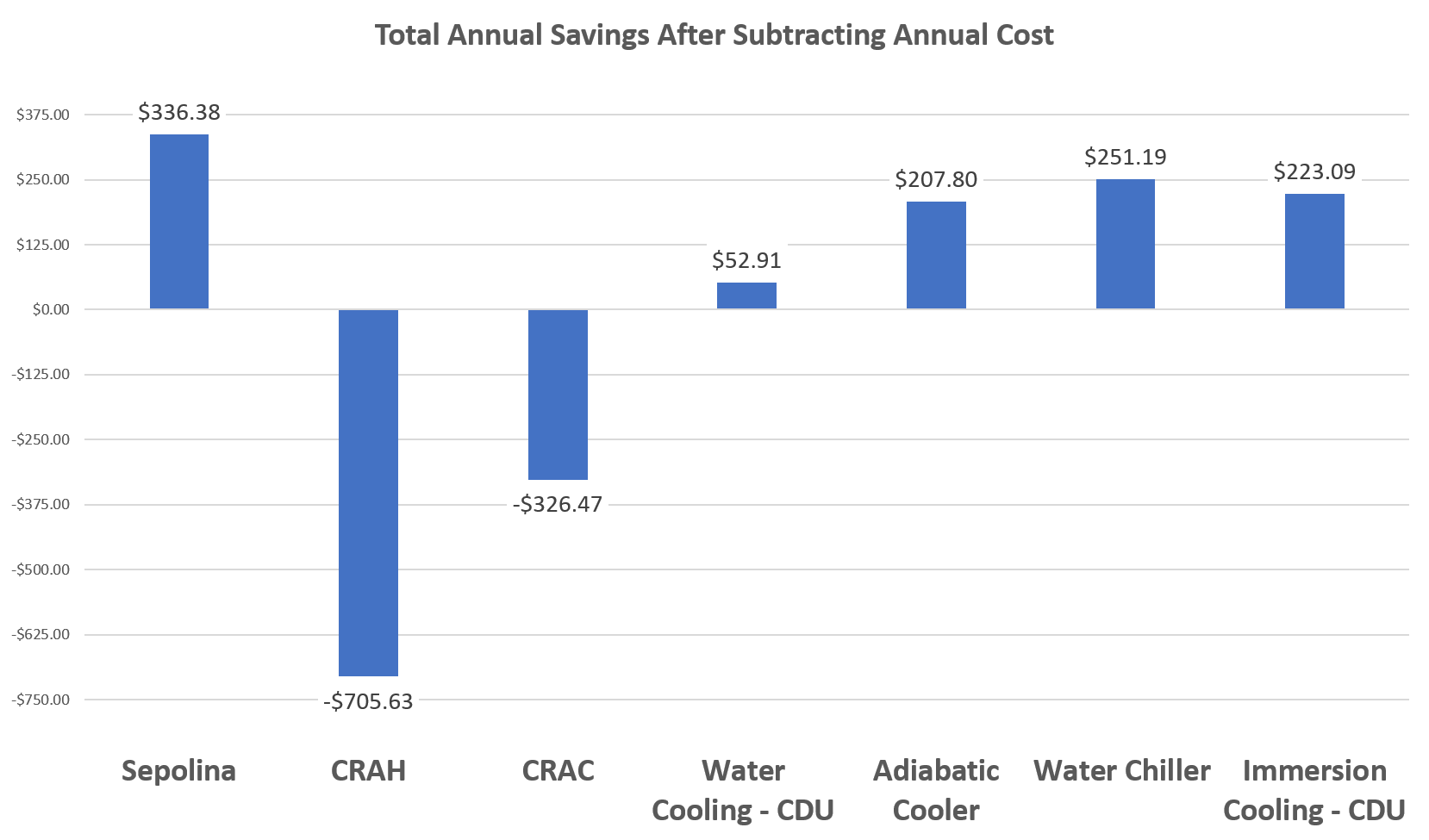
This graph displays the potential annual sum when operating each cooling system. The sum is simply the potential annual cost savings from exhaust recovery subtracted by the annual cost to operate.
As the graph shows, Sepolina provides the greatest potential savings when compared to other cooling methods.
Especially when considering that the savings are not additive. Any cooling systems which requires a secondary system to complete the cooling process, would decrease the potential recovery rate of the secondary system to zero. As the potential energy within the exhaust stream is converted to electricity, the available energy and high temperature decreases leading to lower potential rate of recovery.
In Closing
As shown above, a conversion to our cooling system, provides you the opportunity to not only reduce the number of systems and total consumption of energy for cooling, but also provide greater utilization of current utility power and annual savings via exhaust heat recovery than your current cooling system configuration.